Recent infectious disease outbreaks show that inadequate consideration of social, cultural, political, and religious factors in humanitarian responses has consequences for community acceptance of, and the effectiveness of, response activities. A growing number of studies have focused on the historical, social, cultural, and political determinants of vaccine acceptance, and highlighted the specificities of these dynamics during emergencies. Given the range of disease types and contexts, there is a need to understand different perspectives on vaccines and outbreaks, including: political and economic factors that determine whether and how vaccines can be effectively deployed in an emergency; health system realities closely tied to cultural, policy, and historical developments; and local systems of knowledge to identify community perceptions surrounding vaccine use. This SSHAP Practical Approaches brief can be used by health-care providers/non-governmental organisations (NGOs), national and global-level policymakers, and industry actors to gain social science inputs in vaccine deployment efforts to provide practical solutions to re-occurring challenges, including vaccine refusal.
Briefing
Tools
Social science research for vaccine deployment in epidemic outbreaks
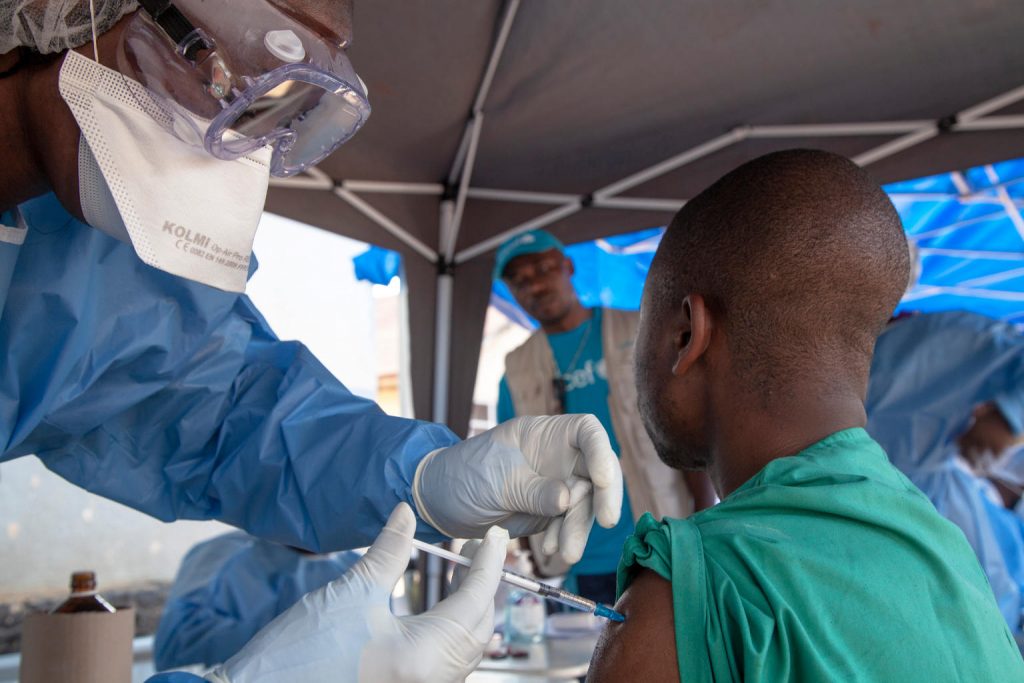
UNICEF/UN0228950/Naftalin
On 10 August 2018, an Ebola vaccination team member (left) prepares to administer the Ebola vaccine in Beni, North Kivu, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
Following the 1 August 2018 announcement by the Government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) of a new Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreak in North Kivu, UNICEF has mobilized its teams to help contain the spread of the disease and protect children. The impact of an outbreak on children can be far reaching. It’s known from earlier outbreaks in the DRC as well as in West Africa that children can be affected in various ways. Children can themselves be infected by the disease, but the impact goes beyond; it impacts their families and communities as children can lose their parents, care-givers and teachers. Access to basic services such as health care and education can become severely compromised. Also, children who are infected or whose relatives are, face stigmatization and social exclusion.
The Congolese Government has activated its response plan and called its partners, including UNICEF, to participate in the response. UNICEF has deployed a team to Beni for the response, including health specialists, communication specialists and a water, sanitation and hygiene specialist from the Ebola-response team in the Province of Equateur. Health, water, sanitation and hygiene and communication supplies have been sent to the affected areas including 300 laser thermometers to monitor the health conditions of people in the affected region and 2,000 kg of chlorine to treat water to help contain the spread of the disease. As at 14 August 2018, UNICEF has installed 35 chlorination points, as well as handwashing units in 45 public places and in health facilities in the affected areas of Beni and Mangina in North Kivu. UNICEF has supported the distribution of prevention posters and leaflets, and worked with communities, in public places and with local radio stations to promote safe hygiene and sanitation
Related content
Case study
SSHAP learning note: Building a localised approach
This learning note shares insights, experiences and lessons from SSHAP's approach to the localisation of its operational responses in sub-Saharan Africa.
Central and East Africa Hub
West Africa Hub
SSHAP
2025
Evidence review
Rapid evidence synthesis: Mpox community protection
This note presents a rapid synthesis of evidence related to community protection in countries affected by the mpox clade 1b outbreak. Synthesising evidence related to community protection for mpox Medline, Africa Journals Online and Global Index Medicus were searched. IFRC,…
SSHAP
2025
Report
Meeting report: The impact of global aid funding cuts on people and programmes in South Sudan
Report of a roundtable with government actors, academics, development partners and journalists in South Sudan on the sweeping impacts on people and programmes of aid cuts and multiple, intersecting crises.
Central and East Africa Hub
SSHAP
2025
Briefing
Key considerations: Home-based care for mpox in Central and East Africa
This brief outlines key considerations on health system requirements for safe and inclusive home-based care for mpox.
Central and East Africa Hub
SSHAP
2025


